Dental Care for Seniors: Addressing Age-Related Oral Health Challenges
As we age, maintaining good oral health becomes increasingly important, yet it often comes with unique challenges. For seniors, dental care is not just about preserving a bright smile—it’s a critical component of overall health and well-being. Age-related changes, such as receding gums, dry mouth, and the side effects of medications, can make seniors more susceptible to dental issues like tooth decay, gum disease, and even tooth loss. These problems, if left unaddressed, can lead to pain, difficulty eating, and even systemic health issues, including heart disease and diabetes.
This article explores the common oral health challenges faced by older adults and provides practical strategies to help seniors maintain healthy teeth and gums. From understanding the impact of medications to adapting dental care routines for physical limitations, we’ll cover everything seniors and their caregivers need to know to prioritize oral health. Regular dental check-ups, preventive care, and daily habits can make a significant difference in ensuring a healthy smile for years to come. Let’s dive into the essential aspects of dental care for seniors and how to overcome age-related challenges effectively.
Common Dental Issues in Older Adults
As we age, our oral health needs change, and seniors often face specific dental challenges that require attention and care. Understanding these common issues is the first step toward preventing and managing them effectively. Here are some of the most prevalent dental problems among older adults:
1. Root Decay
- Causes and Risk Factors:
Receding gums, a natural part of aging, can expose the roots of teeth, making them more vulnerable to decay. Additionally, a diet high in sugar or poor oral hygiene can accelerate this process. - Prevention and Treatment:
Regular brushing with fluoride toothpaste, flossing, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help prevent root decay. Dental treatments like fluoride varnishes or fillings may be necessary if decay is detected.
2. Gum Disease (Periodontal Disease)
- Symptoms and Stages:
Gum disease ranges from mild gingivitis (red, swollen gums) to severe periodontitis, which can lead to tooth loss. Symptoms include bleeding gums, bad breath, and loose teeth. - Impact on Overall Health:
Research shows a strong link between gum disease and systemic conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and stroke. - Management and Treatment:
Professional cleanings, scaling, and root planing can help manage gum disease. Daily brushing and flossing are essential to prevent its progression.
3. Tooth Loss
- Causes and Consequences:
Tooth loss in seniors is often the result of untreated decay or gum disease. Missing teeth can affect nutrition, speech, and self-esteem. - Solutions:
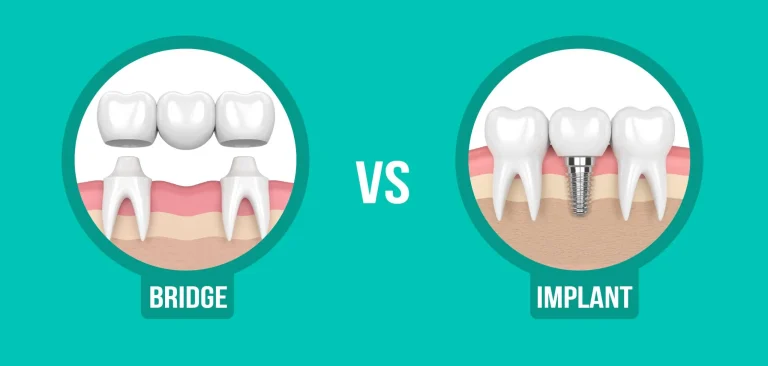
Dentures, bridges, and dental implants are effective options for replacing lost teeth and restoring function.
4. Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
- Causes:
Dry mouth is a common side effect of many medications, including those for blood pressure, depression, and allergies. It can also result from medical conditions like diabetes or Sjögren’s syndrome. - Tips for Managing Dry Mouth:
Staying hydrated, using saliva substitutes, and avoiding caffeine or alcohol can help. Chewing sugar-free gum or using a humidifier at night may also provide relief.
By recognizing these common dental issues, seniors and their caregivers can take proactive steps to maintain oral health. In the next section, we’ll explore how medications can impact oral health and what can be done to mitigate these effects.
Impact of Medications on Oral Health
As we age, it’s common for seniors to take multiple medications to manage various health conditions. While these medications are essential for overall well-being, they can also have unintended effects on oral health. Understanding these impacts and taking steps to address them is crucial for maintaining a healthy mouth.
Common Medications That Affect Oral Health
Many prescription and over-the-counter medications can lead to oral health issues. Some of the most common include:
- Antihistamines: Often used for allergies, these can cause dry mouth.
- Antidepressants: These may reduce saliva production, leading to dry mouth and an increased risk of tooth decay.
- Diuretics: Used to treat high blood pressure, diuretics can also cause dry mouth.
- Pain Medications: Some pain relievers can lead to dry mouth or even gum overgrowth in rare cases.
- Osteoporosis Drugs: Medications like bisphosphonates can affect jawbone health and increase the risk of osteonecrosis of the jaw.
Side Effects of Medications on Oral Health
- Dry Mouth (Xerostomia):
Saliva plays a vital role in neutralizing acids, washing away food particles, and preventing tooth decay. Reduced saliva production can lead to an increased risk of cavities, gum disease, and oral infections. - Gum Overgrowth:
Certain medications, such as anticonvulsants and immunosuppressants, can cause gum tissue to grow excessively, making it harder to clean teeth properly. - Changes in Taste:
Some medications can alter taste perception, which may affect appetite and nutrition. - Increased Risk of Bleeding:
Blood thinners, often prescribed for heart conditions, can make gums more prone to bleeding during brushing or dental procedures.
Strategies to Mitigate These Effects
- Stay Hydrated:
Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help combat dry mouth. - Use Saliva Substitutes:
Over-the-counter saliva substitutes or moisturizing mouth sprays can provide relief. - Chew Sugar-Free Gum:
Chewing gum stimulates saliva production, helping to keep the mouth moist. - Maintain a Consistent Oral Care Routine:
Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily are essential to prevent decay and gum disease. - Consult Your Dentist and Doctor:
Inform your dentist about all medications you’re taking. They may recommend adjustments to your oral care routine or suggest alternative medications with fewer side effects.
By being aware of how medications can impact oral health, seniors can take proactive steps to minimize these effects. In the next section, we’ll discuss adaptations for seniors with physical limitations, ensuring that everyone can maintain good oral hygiene regardless of mobility or dexterity challenges.
Adaptations for Seniors with Physical Limitations
As we age, physical limitations such as arthritis, reduced dexterity, or mobility issues can make it challenging to maintain proper oral hygiene. However, with the right tools and techniques, seniors can continue to care for their teeth and gums effectively. Here are some practical adaptations to help overcome these challenges:
Challenges Faced by Seniors with Physical Limitations
- Arthritis: Pain and stiffness in the hands can make brushing and flossing difficult.
- Reduced Mobility: Limited movement may make it hard to reach the sink or hold dental tools.
- Vision Problems: Poor eyesight can make it difficult to see plaque or food particles, leading to inadequate cleaning.
Adaptive Dental Tools and Techniques
- Electric Toothbrushes:
Electric toothbrushes are easier to grip and require less manual effort, making them ideal for seniors with arthritis or limited hand strength. Many models also come with timers to ensure thorough brushing. - Floss Holders and Water Flossers:
Traditional flossing can be challenging for those with dexterity issues. Floss holders or water flossers (like Waterpik) provide an easier and more effective way to clean between teeth. - Toothbrushes with Larger Handles:
Toothbrushes with ergonomic, non-slip handles can make brushing more comfortable for seniors with grip issues. - Magnifying Mirrors:
For those with vision problems, magnifying mirrors can help seniors see their teeth and gums more clearly, ensuring better cleaning.
Tips for Caregivers Assisting Seniors with Oral Care
- Be Patient and Supportive:
Encourage seniors to take their time and offer assistance when needed. - Use Step-by-Step Guidance:
Break down the oral care routine into simple steps to make it less overwhelming. - Ensure Accessibility:
Make sure the bathroom is set up to accommodate mobility aids like walkers or wheelchairs. Consider placing oral care items within easy reach. - Regularly Check for Issues:
Caregivers should monitor seniors’ oral health for signs of problems like bleeding gums, bad breath, or loose teeth and schedule dental visits as needed.
Encouraging Independence
While assistance may be necessary, it’s important to encourage seniors to maintain as much independence as possible. Adaptive tools and techniques can empower them to take control of their oral health, boosting their confidence and overall well-being.
By making small adjustments to their oral care routine, seniors with physical limitations can continue to maintain healthy teeth and gums. In the next section, we’ll explore the importance of regular dental check-ups and how they contribute to overall health.
Importance of Regular Dental Check-ups for Overall Health
Regular dental check-ups are a cornerstone of maintaining good oral health, especially for seniors. These visits are not just about keeping teeth clean—they play a vital role in preventing serious health issues and ensuring early detection of problems. Let’s explore why regular dental check-ups are so important for seniors and how they contribute to overall well-being.
Link Between Oral Health and Systemic Conditions
Research has shown a strong connection between oral health and overall health. Poor oral hygiene can contribute to or exacerbate systemic conditions, including:
- Heart Disease: Gum disease has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease and stroke due to inflammation and bacteria entering the bloodstream.
- Diabetes: Gum disease can make it harder to control blood sugar levels, while diabetes can increase the risk of gum disease, creating a vicious cycle.
- Respiratory Infections: Bacteria from the mouth can be inhaled into the lungs, leading to infections like pneumonia, which is particularly dangerous for seniors.
- Osteoporosis: This condition can weaken the jawbone, leading to tooth loss and other dental issues.
Frequency of Dental Visits Recommended for Seniors
- General Recommendation:
Most dentists recommend visiting every six months for a routine check-up and cleaning. However, seniors with specific oral health issues may need to visit more frequently. - Personalized Plans:
A dentist can create a customized schedule based on an individual’s oral health needs, medical history, and risk factors.
What to Expect During a Senior Dental Check-up
- Comprehensive Exam:
The dentist will check for signs of tooth decay, gum disease, oral cancer, and other issues. They may also evaluate the fit of dentures or other dental appliances. - Professional Cleaning:
A dental hygienist will remove plaque and tartar buildup, which can’t be eliminated through regular brushing and flossing. - Oral Cancer Screening:
Seniors are at a higher risk for oral cancer, so regular screenings are essential for early detection and treatment. - X-rays and Diagnostic Tests:
These may be used to identify problems that aren’t visible during a visual exam, such as bone loss or hidden decay.
Benefits of Regular Dental Check-ups
- Early Detection of Problems:
Catching issues like cavities, gum disease, or oral cancer early can prevent more serious complications down the line. - Prevention of Tooth Loss:
Regular cleanings and exams help maintain healthy teeth and gums, reducing the risk of tooth loss. - Improved Overall Health:
By addressing oral health issues, seniors can reduce their risk of developing or worsening systemic conditions. - Peace of Mind:
Knowing that their oral health is being monitored can give seniors and their caregivers confidence and reassurance.
Overcoming Barriers to Dental Care
- Transportation Issues:
Seniors with mobility challenges can explore options like community transportation services or mobile dental clinics. - Financial Concerns:
Medicare typically doesn’t cover routine dental care, but supplemental insurance or discount dental plans can help make care more affordable. - Dental Anxiety:
For seniors who feel anxious about dental visits, finding a compassionate dentist who specializes in treating older adults can make a big difference.
Regular dental check-ups are an essential part of maintaining not just oral health, but overall health as well. In the next section, we’ll provide practical preventive measures and daily oral care tips to help seniors keep their smiles healthy between visits.
Preventive Measures and Daily Oral Care Tips
Maintaining good oral health as a senior requires a combination of professional care and consistent daily habits. By adopting preventive measures and following a thorough oral care routine, seniors can reduce their risk of dental problems and enjoy a healthier smile. Here are some practical tips to help seniors take charge of their oral health:
Brushing and Flossing Techniques Tailored for Seniors
- Brushing Twice a Day:
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to gently clean teeth and gums. Electric toothbrushes can be especially helpful for seniors with limited dexterity. - Technique: Hold the brush at a 45-degree angle to the gums and use small, circular motions. Don’t forget to brush the tongue to remove bacteria and freshen breath.
- Flossing Daily:
Flossing removes plaque and food particles from between teeth, where a toothbrush can’t reach. - Adaptive Tools: For seniors who find traditional flossing difficult, floss holders or water flossers can make the process easier and more effective.
Importance of Fluoride and Antimicrobial Mouth Rinses
- Fluoride:
Fluoride strengthens tooth enamel and helps prevent decay. Seniors can use fluoride toothpaste or ask their dentist about fluoride treatments during check-ups. - Antimicrobial Mouth Rinses:
These rinses can help reduce bacteria in the mouth, preventing gum disease and bad breath. Look for alcohol-free options to avoid dry mouth.
Dietary Considerations for Maintaining Oral Health
- Foods to Avoid:
Limit sugary and acidic foods and beverages, which can contribute to tooth decay and enamel erosion. - Foods That Promote Oral Health:
- Calcium-Rich Foods: Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods help strengthen teeth and bones.
- Crunchy Fruits and Vegetables: Apples, carrots, and celery can help clean teeth naturally and stimulate saliva production.
- Water: Drinking water throughout the day helps wash away food particles and keeps the mouth hydrated.
Additional Tips for Seniors
- Stay Hydrated:
Dry mouth is a common issue for seniors, so drinking plenty of water is essential. Chewing sugar-free gum or using saliva substitutes can also help. - Quit Smoking:
Smoking increases the risk of gum disease, tooth loss, and oral cancer. Quitting smoking can significantly improve oral and overall health. - Protect Your Teeth:
If you grind your teeth at night, consider using a mouthguard to prevent damage.
Regular Dental Visits
- Schedule Check-ups Every Six Months:
Regular dental visits are crucial for catching problems early and maintaining oral health. - Communicate with Your Dentist:
Inform your dentist about any changes in your health, medications, or oral care routine so they can provide personalized recommendations.
By following these preventive measures and daily care tips, seniors can maintain healthy teeth and gums, reducing their risk of dental problems and improving their quality of life. In the next section, we’ll wrap up with a conclusion and a call to action to encourage seniors to prioritize their oral health.
Conclusion
As we age, oral health becomes an increasingly important aspect of overall well-being. Seniors face unique challenges, from common dental issues like gum disease and dry mouth to the impact of medications and physical limitations. However, with the right knowledge, tools, and habits, these challenges can be effectively managed.
Regular dental check-ups, adaptive oral care tools, and a consistent daily routine are key to maintaining a healthy smile. By prioritizing oral health, seniors can not only preserve their teeth and gums but also reduce their risk of systemic health issues like heart disease and diabetes.
Final Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Smile in Later Years
- Stay Consistent: Brush twice a day, floss daily, and use fluoride products to protect your teeth.
- Adapt as Needed: Use tools like electric toothbrushes, floss holders, or water flossers to make oral care easier.
- Stay Informed: Keep your dentist updated about any changes in your health or medications.
- Prioritize Prevention: Regular dental visits and a healthy diet can go a long way in preventing problems before they start.
Your oral health is a vital part of your overall health and quality of life. If it’s been a while since your last dental check-up, now is the perfect time to schedule an appointment. Don’t wait for problems to arise—take proactive steps to maintain your smile and well-being.
If you found this article helpful, share it with a friend or family member who might benefit from these tips. Have questions or experiences to share? Leave a comment below—we’d love to hear from you!
Remember, a healthy smile is a lifelong asset. Let’s work together to keep it bright and strong for years to come.
FAQs
Q: Why is dental care especially important for seniors?
A: Seniors are more susceptible to oral health problems like gum disease, dry mouth, and tooth loss due to age-related changes and potential underlying health conditions.
Q: What are some common oral health issues faced by seniors?
A: Common issues include dry mouth (xerostomia), gum disease (periodontitis), tooth decay, root decay, oral cancer, and denture-related problems.
Q: What causes dry mouth in seniors, and how can it be managed?
A: Dry mouth can be caused by medications, certain medical conditions, or aging itself. Management includes staying hydrated, using saliva substitutes, and avoiding sugary drinks.
Q: How does gum disease affect seniors, and what are the treatment options?
A: Gum disease can lead to tooth loss and is linked to other health problems. Treatment options include scaling and root planing, antibiotics, and, in severe cases, surgery.
Q: Are dentures the only option for replacing missing teeth?
A: No, dental implants and bridges are also viable options for replacing missing teeth. They offer more stability and can improve chewing ability.
Q: What should seniors look for in a denture adhesive?
A: Seniors should look for denture adhesives that are ADA-accepted, provide a strong hold, and are easy to apply and remove. Consulting with a dentist for recommendations is also advisable.
Q: How does diet affect senior oral health?
A: A balanced diet low in sugar and acidic foods is crucial. Seniors should consume calcium-rich foods and stay hydrated for optimal oral health.
Q: How often should seniors visit the dentist?
A: Seniors should visit the dentist regularly, typically every six months, or more frequently if they have existing oral health problems.
Q: What are the warning signs of oral cancer that seniors should be aware of?
A: Warning signs include sores that don’t heal, lumps or thickening in the mouth, difficulty swallowing, and white or red patches. Any of these symptoms should be evaluated by a dentist or doctor promptly.
Q: Are there any special considerations for seniors with medical conditions when it comes to dental treatment?
A: Yes, seniors with conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or osteoporosis may require modified treatment plans and closer monitoring during dental procedures. It’s important to inform the dentist about all medical conditions and medications.